What is Machine Learning?#
Have you ever wondered how Netflix always seems to know exactly what movie or TV show to recommend next? The secret lies in machine learning. By analyzing your viewing history, ratings, and even the habits of viewers with similar tastes, Netflix’s algorithms detect patterns and predict which content you might enjoy. It’s not just random suggestions, it’s a sophisticated system that processes vast amounts of data to tailor recommendations for you, ensuring that your next binge-watching session feels perfectly curated just for you.
But what is machine learning? Machine learning is a branch of artificial intelligence that enables computers to learn from data and make predictions or decisions without being explicitly programmed. Rather than relying on fixed instructions, machine learning algorithms analyze vast amounts of data to identify meaningful patterns and predict outcomes.
Types of learning#
Machine learning can be categorized into three main types based on the way the model learns from data:
Supervised learning: Uses labeled data to train models, making predictions or decisions based on examples (e.g., predicting mental health scores based on questionnaire responses).
Unsupervised learning: Finds patterns or structures in unlabeled data (e.g., clustering individuals based on similar traits or behaviors).
Reinforcement learning: Involves an agent interacting with an environment, learning through trial and error with feedback from its actions.
In this course, we will focus on the first two types of learning. If you are interested in reinforcement learning, you can find a nice introduction here.
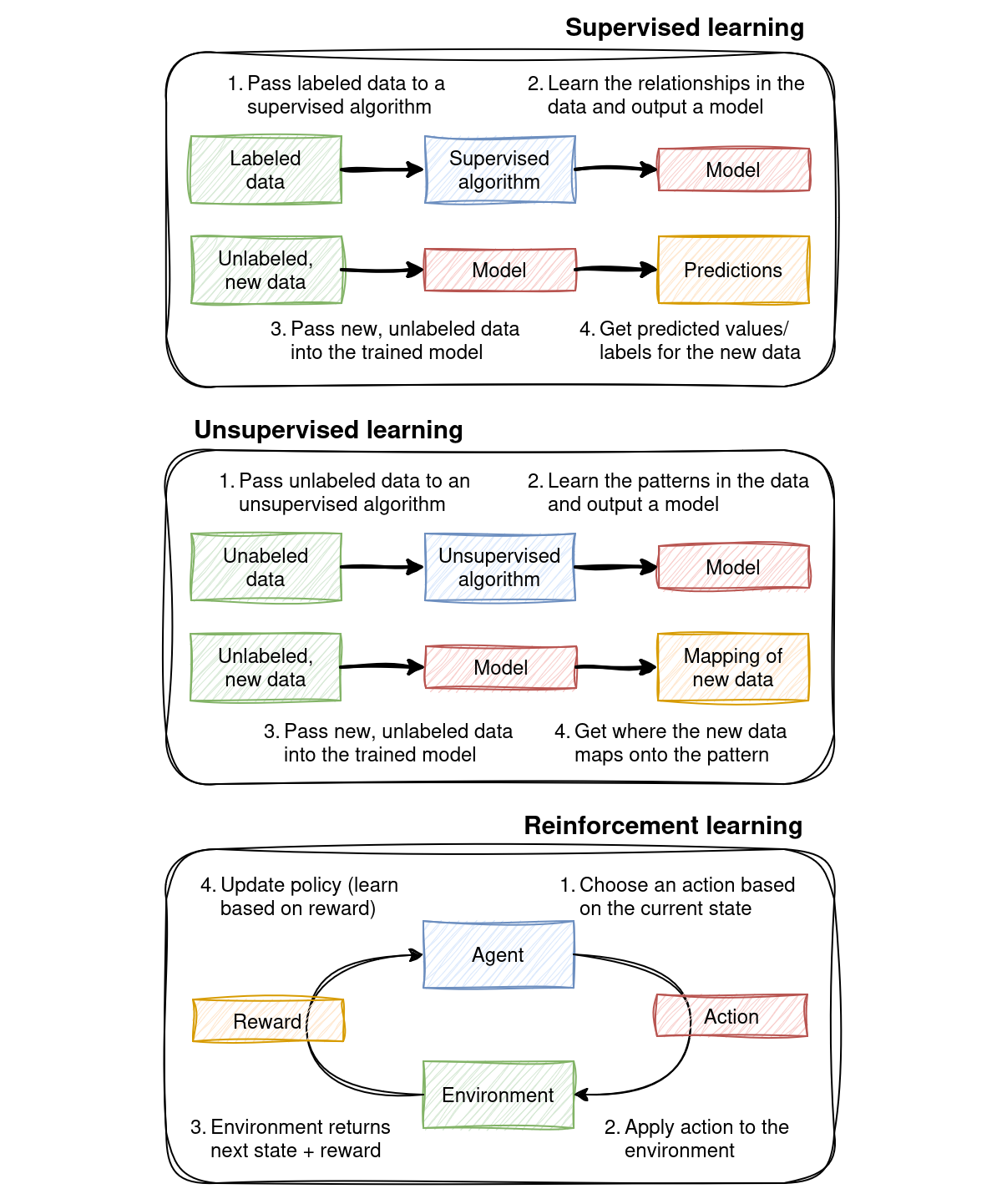
Fig. 1 Three main types of machine learning: Supervised, unsupervised, and reinforcement learning.#
Classes of algorithms#
In addition to the type of learning, algorithms can also be categorized based on the type of data that needs to be predicted:
Type of data |
Type of learning |
Type of learning |
|---|---|---|
Supervised learning |
Unsupervised learning |
|
Qualitative (categorical) |
Classification |
Clustering |
Quantitative (numerical) |
Regression |
Dimensionality reduction |
Assessing performance#
Assessing the performance of a machine learning model is crucial to ensure its accuracy and applicability. Important evaluation metrics for this are:
Mean Squared Error (MSE): Measures the average squared difference between predicted and actual values (regression tasks).
Missclassification Error: Describes the proportion of incorrectly predicted class assignments (classification tasks).
There are many more performance (accuracy) metrics (which you might already know), such as the Root Mean Squared Error (RMSE), R-Squared (R²), Precision, or a confusion matrix. You will get to know some of them in the following weeks.
In addition, techniques such as cross-validation help to estimate the performance of a model in an unbiased manner. Cross-validation splits the dataset into training and testing subsets, reducing the risk of overfitting and proving a better assessment of how the model will perform on unseen data. We will explore this topic in the Resampling Strategies session.

